Formulation of the bark extract of Michelia champaca to control Curvularia leaf spot in rice (Oryza sativa L.)
Main Article Content
Abstract
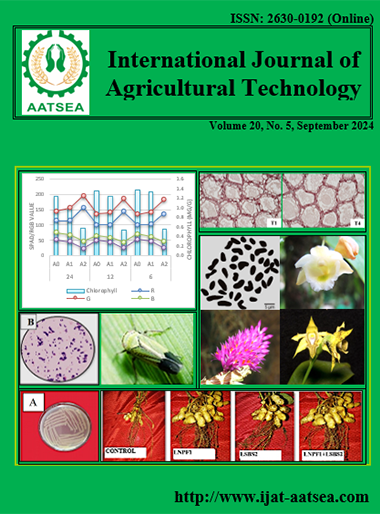
The formulation of a botanical fungicide with the active ingredient of Michelia champaca bark extract to control the growth of Curvularia verruculosa, which causes leaf spot disease in rice plants in the greenhouse was investigated. The results showed that the formula for M. champaca bark extract at a concentration of 1.5% (w/v) was reduced the disease intensity of Curvularia leaf spot by up to 66.01% at 24 days after application. This formula was also able to increase the number of tillers and leaf chlorophyll levels by 40.05% and 41.18%, respectively at 63 days after planting. The formula of M. champaca bark extract at a concentration of 1.5% (w/v) increased the yield of harvested dry grain by 89.26%.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Abdel-Ghany, T. M., Abdel-Rahman, M. S., Moustafa, E. N., Al Abboud, M. A. and Nadeem, I. E. (2015). Efficacy of botanical fungicides against Curvularia lunata at molecular levels. J. Plant Pathol & Microb, 6:1-7.
Bawa, I G. A. G. (2019). Active compounds and fungisidic activity of the bark extract of Michelia alba to Curvularia verruculosa caused leaf spot disease in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). (Dissertation). University of Udayana, Bali Indonesia.
Bawa, I G. A. G. (2021). Exploration of plant extracts that show antifungal activity against the Curvularia verruculosa fungal that causes leaf spot disease in rice plants (Oryza sativa L.). Journal of Chemistry, 15:8-11.
Bawa, I G. A. G., Santi, S. R., Rita, W. S., Suryanadi, O. and Indyan, G. (2024). Active compounds of Michelia champaca bark extract against Curvularia verruculosa fungi causing leaf spot disease in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Journal of Applied and Natural Science, 16:420-426.
Choudhury, D., Anand, Y. R., Kundu, S., Nath, R., Kole, R. K. and Saha, J. (2017). Effect of plant extracts against sheath blight of rice caused by Rhizoctonia solani. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 6:399-404.
Kagale, S., Marimuthu, T., Thayumanavan, B., Nandakumar, R. and Samiyappan, R. (2005). Antimicrobial activity and induction of systemic resistance in rice by leaf extract of Datura metel against Rhizoctonia solani and Xanthomonas pv oryzae. Physiological and Mole. Plant Pathol, 65:91-100.
Kumar, S., LaI, A. A., Kumar, N., Jaiswal, S., Kumar, H., Kumar, A. and Kumar, M. (2017). Effect of biocontrol agents and botanicals against blast of paddy caused by Pyricularia oryzae. International Journal of Chemical Studies, 5:314-318.
Manjappa, K. (2015). Evaluation of antifungal properties of eupatorium (Chromolaena odorata L.) plant extract againts Pyricularia oryzae causing blast disease in rice crop. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Science & Technology, 5:79-81.
Nguefack, J., Wuff, G. E., Dongmo, J. B. L., Fouelefack, F. R., Fotio, D., Mbo, J. and Torp, J. (2013). Effect of plant extracts and an essential oil on the control of brown spot disease, tillering, number of panicles and yield increase in rice. Eur J Plant Pathol., 137:871-882.
Omezzine, F., Daami-Remadi, M., Rinez, A., Ladhari, A. and Haouala, R. (2011). In vitro assessment of Inula spp. organic extracts for their antifungal activity against some pathogenic and antagonistic fungi. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 5:3527-3531.
Pandey, S. (2018). Effect of botanicals for management of leaf blast and enhancing yield traits in rice. Current Botany, 9:17-21.
Perez, C. E. A., Rodrigues, F. A., Moreira, W. R. and DaMatta, F. M. (2014). Leaf gas exchange and chlorophyll a fluorescence in wheat plants supplied with silicon and infected with Pyricularia oryzae. J. Phytopathol., 104:143-149.
Rahman, M. (1992). Study on the seed-borne fungi and their control with botanical and chemical fungicide on five local boro varieties of rice. (Thesis). Dept. of Plant Pathology, BAU, Mymensingh.
Rios, J., Rodrigues, F. D., Debona, D. and Silva, L. (2014). Photosynthetic gas exchange in leaves of wheat plants supplied with silicon and infected with Pyricularia oryzae. Acta Physiol. Plant, 36:371-379.
Sinaga, M. S. (2006). The fundamental of diseases plant. Bogor-Indonesia: Penebar Swadaya.
Thi, Q. N., Lemtukei, D., Kihara, J. and Ueno, M. (2016). Efficacy of plant extracts against the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Bull. Fac. Life Env. Sci. Shimane Univ., 21:13-16.
West, J. S., Bravo, C., Oberit, R., Lemaire, D., Moshou, D. and McCartney, H. A. (2003). The potential of optical canopy measurement for targeted control of field crop diseases. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 41:593-614.
Yoon, M. Y., Cha, B. and Kim, Jin-Cheol. (2013). Recent trends in studies on botanical fungicides in agriculture. Plant Pathol J., 29:1-9.